Don't Let Infertility Get in the Way of Parenthood

Every couple dreams of starting their own family – to be able to bear a child, nurture them and see them grow is one of those unique goals that every couple hopes to achieve someday. However, when this long-awaited dream stumbles upon a barrier in the form of infertility, it can be very frustrating. But hey, don’t lose hope yet, because there is a solution.
Want to know more? We reveal a very effective fertility treatment to make your parenthood dreams a reality.
In-Vitro Fertilisation
In-vitro fertilisation or IVF is a type of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART). ARTs are clinical methods used to treat infertility, using procedures involving both egg and sperm.
This week’s blog explores the ART method – ‘In-vitro Fertilisation’ (IVF). With its usual success rates ranging from 35%-55%, it has become a very popular fertility treatment method for couples worldwide and, increasingly, in Sri Lanka too.
IVF uses a combination of medicines and surgical procedures to aid the fertilisation process between sperm and egg cells. Additionally, after fertilisation occurs, IVF helps the fertilised egg to implant in your uterus. Babies born using IVF (popularly known as test-tube babies) have been healthy and successfully delivered using this method.


Is IVF the answer for you?
IVF treatment is designed for couples with infertility and genetic problems. Other medical conditions and issues for which IVF can be used are:
- Fallopian tube damage/blockage
- Ovulation disorders
- Endometriosis – When tissue similar to the uterus lining grows outside the uterus
- Uterine fibroids – Benign tumours in the uterus
- Impaired sperm production/function – Low sperm mobility and functionality
- Low sperm count
- Unexplained infertility
- Fertility preservation for cancer treatment – IVF is suited for you if you are about to undergo cancer treatment (chemotherapy/radiation) that could affect your fertility. IVF can help you store your eggs and embryos for later use.
The IVF Process - How does it work?
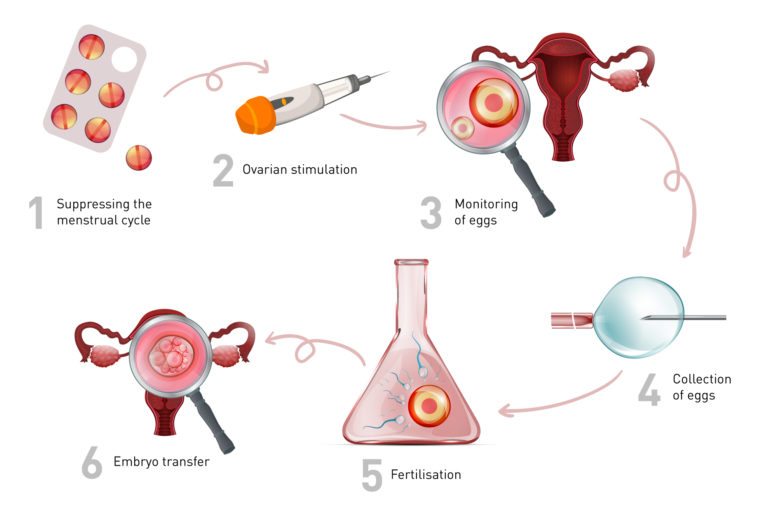
Let’s break down the IVF process. There are 6 main stages.
Stage 1: Suppressing the menstrual cycle
This is the first step of IVF. As you begin your period, hormone tests and an ultrasound scan will be conducted. Afterwards, you will be prescribed birth control pills for 2-4 weeks to suppress ovarian hormones that prevent ovulation (the process of the female body releasing egg cells). This is done to synchronise the eggs to ensure that more eggs will become mature during the second stage. Finally, once birth control pills are stopped, most women get their periods again.
Stage 2: Ovarian stimulation
Synthetic hormones and medications will be used to stimulate your ovaries. This is crucial as IVF requires a woman to develop multiple eggs rather than a single egg (the typical amount a woman produces each month). Multiple eggs are needed to ensure the success of the treatment, as some eggs may not fertilise or develop normally after fertilisation.
Stage 3: Monitoring of eggs
This stage is when your doctor monitors the development of the eggs in your ovaries before collecting them for fertilisation. Vaginal ultrasound scans and blood tests will be done to assess this.
Stage 4: Collection of eggs
Once the doctor confirms that your eggs are mature and ready for collection, you would have to undergo a clinical procedure to retrieve your eggs from your ovaries. The mature eggs are removed using an ultrasound probe and a thin needle which is inserted into your vagina. This surgical procedure usually takes about 20 minutes. After this process, mature eggs are placed in a nutritive liquid and incubated.
Stage 5: Fertilisation
Fertilisation is when the collected egg and sperm samples are mixed and incubated. After a few days, embryos (fertilised eggs) may develop.
Stage 6: Embryo transfer
The final stage of IVF involves placing the fertilised eggs into the woman’s uterus. The doctor will place the embryos in your uterus using various tools such as catheters and a syringe. After 2 weeks, couples are advised to take a pregnancy test to check whether they are pregnant. If the embryo implants in your uterus lining, this will then indicate a successful pregnancy.
Cost and Price of IVF Treatments
Although IVF has considerable success rates, it is the most expensive assisted reproductive treatment. However, it has been the most sought-out infertility treatment method by most couples due to its success rates, despite its high prices.
Benefits of IVF

So, now that you know what IVF is and what happens in its process, is it worth it? Let’s find out.
- Improved chances of having a healthy baby
Did you know IVF procedures involve conducting tests like preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) on a fertilised embryo before transferring it to the uterus? These tests assess any abnormal number of chromosomes and risks of inherited genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis or Tay-Sachs Disease in embryos. So if you use IVF, the chances of your baby being healthy is higher.
- Better chances of conception
If natural reproductive methods haven’t helped you and your partner conceive, it’s maybe the right time to look into IVF treatments. With success rates ranging between 35%-55%, it increases a woman’s chances of conception due to it being conducted in a highly controlled process. Furthermore, IVF enhances the chances of a woman being pregnant beyond her 20s too.
- Lower risk of miscarriage
Since tests like PGT are conducted during IVF, they can identify the most genetically viable embryos. Miscarriages mainly occur due to chromosome abnormalities, so IVF’s capability to ensure that the best embryos are placed in a woman’s uterus reduces the possible risk of miscarriages caused by genetic and chromosomal abnormabilities.
- More control over family planning
Advancements in modern science, such as IVF, are unquestionably great innovations. If you are a busy couple or feel that you aren’t ready for parenthood yet, IVF lets you decide when you want to conceive by cryopreserving your eggs or embryos until you are ready for parenthood.
Risks of IVF Treatments
- Multiple births
If more than one embryo is placed in your uterus, the risk of having multiple births increases. This could cause complications with early labour and the baby’s weight.
- Premature births and low birth weight
Previous research proves that IVF slightly increases the chances of a baby being born early or with a low birth weight, which could be unhealthy for the baby.
3. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
This occurs when certain hormones and medications are used to induce ovulation during IVF, and the ovaries become swollen and painful. Symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and bloating would occur.
4. Miscarriage
Miscarriage can be a very unpleasant experience. However, despite the advanced tests conducted in IVF, due to various issues in fertilisation, such as the possibility of chromosomal variation and more, even IVF has a similar risk of miscarriage – a percentage similar to women conceiving naturally. Therefore, a successful conception cannot be guaranteed entirely, even with this procedure.
Other risks include possible bleeding and damage to the bowel, bladder and blood vessels during the collection of eggs and an increased risk of cancer and ectopic pregnancy (when the embryo implants outside the uterus). It is vital to be educated about the benefits and risks of IVF to decide whether IVF is the right option for you.
From where can I get IVF treatment?
If you are interested in seeking IVF treatments, you must consult a gynaecologist who will provide you with the necessary advice and information. In addition, they will diagnose any medical conditions or issues that have prevented you from successfully conceiving before recommending this treatment option.
You can consult a gynaecologist via oDoc to discuss comprehensively with them whether IVF is right for you. They will help you achieve your dream of becoming a parent and educate you on the best option for conception.

References
- In vitro fertilisation, Mayo Clinic
- In vitro fertilisation process, Midwest Reproductive (PA)
Similar Articles...

Let’s talk flu, its prevention and home remedies.
Boo-ger season is here! Let’s begin by defining flu (short term for influenza) because it’s usually misunderstood as fever or cold. Flu is a common

Menopause Brain Fog is real: A Simple Guide with Symptoms and Treatment
Menopause Brain Fog is real: A Simple Guide with Symptoms and Treatment Women in their 40s and 50s who are just entering the end of

How to Keep Work Stress from Taking Over Your Life
How to Keep Work Stress from Taking Over Your Life In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, work stress has become an all-too-common problem that affects