A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding HIV and AIDS
In today’s world, health awareness plays a pivotal role in promoting overall well-being. One of humanity’s most significant challenges is the spread of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and the subsequent development of AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). While these terms are often used interchangeably, it’s essential to understand their differences, symptoms, and impact on individuals and societies. This guide will delve into the intricacies of HIV and AIDS, shedding light on their symptoms, distinctions, and prevention.
Understanding HIV and AIDS
HIV: The Virus Behind the Syndrome
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a lentivirus that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which play a crucial role in fighting infections. HIV weakens the immune system over time, leaving the body vulnerable to various illnesses and infections. The virus is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual contact, sharing of needles among drug users, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
AIDS: The Advanced Stage
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the final stage of HIV infection. Individuals with AIDS have severely compromised immune systems, making them susceptible to opportunistic infections, cancers, and other complications. The transition from HIV to AIDS typically occurs when the CD4 cell count falls below a certain level or when specific opportunistic infections or cancers develop.
Key Differences between HIV and AIDS
It’s essential to differentiate between HIV and AIDS to understand their progression and impact correctly.
HIV Infection Stage: HIV refers to the initial stage of the viral infection, during which the virus replicates in the body. A person with HIV may or may not show noticeable symptoms and can lead a relatively everyday life with proper medical care.
AIDS Development: AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection. It is characterised by a significantly weakened immune system and specific opportunistic infections or cancers. Without proper medical intervention, AIDS can be life-threatening.
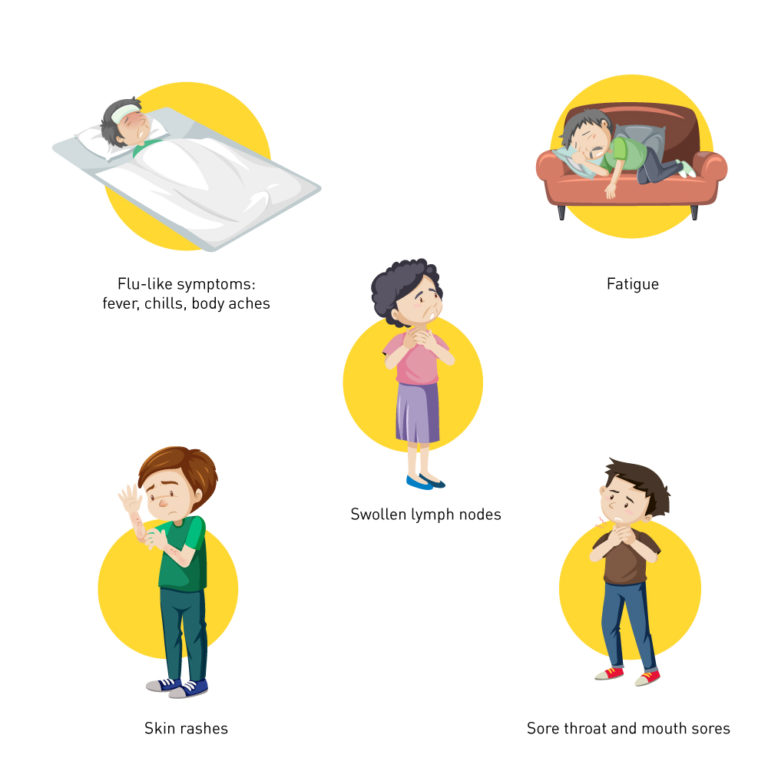
Symptoms of HIV and AIDS
HIV Symptoms: Early Warning Signs
In the early stages of HIV infection, individuals may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. However, many people with HIV remain asymptomatic for years, so regular testing is crucial, especially for individuals engaging in high-risk behaviour.
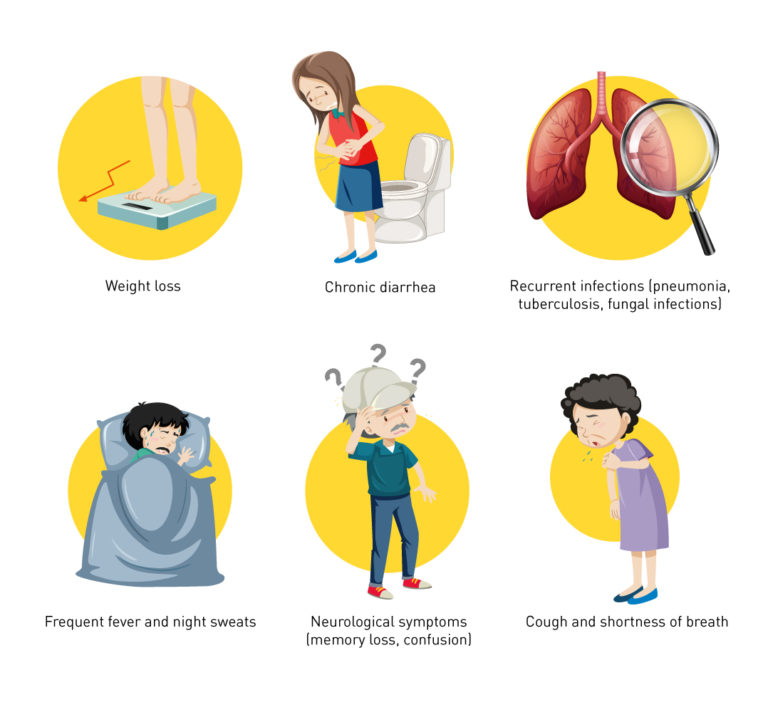
AIDS Symptoms: Advanced Stage Indicators
As HIV progresses to AIDS, the symptoms become more severe. Common symptoms include chronic diarrhea, rapid weight loss, persistent fever, night sweats, and extreme fatigue. Various opportunistic infections like pneumonia, tuberculosis, and certain cancers may also occur.
In Sri Lanka, 87% were reported among key populations, including sex workers, men who have sex with men, and people who inject drugs.
Preventive Measures and Treatment Options
Preventing HIV Transmission
Prevention is a crucial aspect of curbing the spread of HIV. Using condoms during sexual intercourse, getting regular HIV tests, avoiding sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, and opting for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are effective ways to prevent transmission.
HIV Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can significantly slow the virus’s progression. ART involves a combination of medications that suppress the viral load in the body, allowing the immune system to recover and function more effectively.
Understanding the nuances of HIV and AIDS is essential for creating a more informed and compassionate society. While medical advancements have transformed HIV from a life-threatening disease to a manageable condition, it’s crucial to remember that prevention is still the most potent weapon in our arsenal. Regular testing, safe practices, and stigmatisation efforts are critical to reducing the impact of HIV and AIDS in Sri Lanka and worldwide. By staying educated and empathetic, we can continue to make strides toward a healthier future for all.
Remember that symptoms can vary, and some people may not experience noticeable symptoms. If you’re concerned about HIV, consult a Gynecologist or Urologist from the comfort of your home via oDoc
Sources
HIV and AIDS.” World Health Organization (WHO), 13 July 2023, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids
Vinetz, Joseph. “HIV and AIDS: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, and More.” Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/hiv-aids.
Untitled.” National STD/AIDS Control Programme, http://www.aidscontrol.gov.lk/images/publications/guidelines/handbook_on_hiv_aids_for_public_healt_hcare_workers.pdf.
Similar Articles...

Let’s talk flu, its prevention and home remedies.
Boo-ger season is here! Let’s begin by defining flu (short term for influenza) because it’s usually misunderstood as fever or cold. Flu is a common

Menopause Brain Fog is real: A Simple Guide with Symptoms and Treatment
Menopause Brain Fog is real: A Simple Guide with Symptoms and Treatment Women in their 40s and 50s who are just entering the end of

How to Keep Work Stress from Taking Over Your Life
How to Keep Work Stress from Taking Over Your Life In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, work stress has become an all-too-common problem that affects
















